Module Tools Documentation
这里是工具模块的文档。
您可以在这里找到关于工具模块的详细信息。
Sure, here's the translated text: ```html 你即将设置一个 API,它接收查询,并像一个知识丰富的助手一样,为您解答有关 Jira 工单的问题。 ```
Sure, here's the translated text in simplified Chinese within the HTML structure: ```html
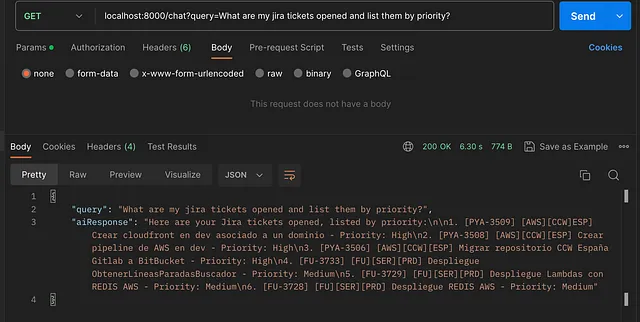
查询:我的JIRA工单已打开并按优先级列出它们?
```Sure, here's the translation in simplified Chinese, keeping the HTML structure: ```html
Ai 回复:「这是您的 Jira 开放工单,按优先级列出:[工单列表]。」
```Sure, here's the translation in simplified Chinese while keeping the HTML structure: ```html
AI响应可能在每次调用之间有所不同。
```
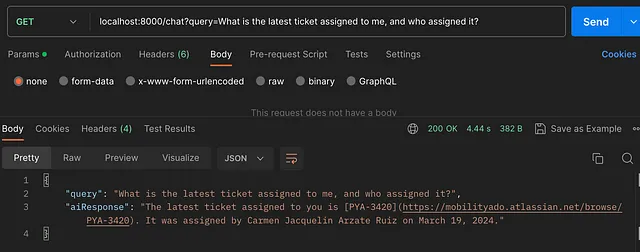
Sure, here's the translation in simplified Chinese: ```html 查询:最新分配给我的票务是什么,由谁分配? ```
Sure, here is the translated text in simplified Chinese: AI回复:“分配给您的最新工单号是PYA-3420,标题为“[TRA][PYA][REQ]Despliegue de versión Coldstart Monedero QA AWS”。该工单是由XXX分配给您的。”
Sure, here's the translated text in simplified Chinese, keeping the HTML structure: ```html
AI响应可能会因每次调用而有所不同。
```
Sure, here's the translated text in simplified Chinese: ```html
Sure, here's the translated text in simplified Chinese while keeping the HTML structure: ```html
为什么费心?因为私有API是您的入口,可以访问您的应用程序所依赖的大量数据,例如Jira中的项目更新或CRM中的客户详细信息。但是要获取这些数据可能感觉像是在迷宫中航行。这就是我们的语言模型发挥作用的地方,它可以将您的普通英语问题转化为解锁这一宝藏所需的技术术语,同时让这一切感觉像是轻松地在喝咖啡时聊天一样。
```Sure, here's the translated text: ```html
关键在于更聪明地工作,而不是更努力地工作。无论您是在编码还是领导团队,将LLMs与私有API集成可以加速您的生产力。准备改变您与技术工具互动的方式了吗?让我们深入探讨并发现如何做到!
```LangChain介绍 🦜️🔗
```Sure, here's the translated text in simplified Chinese, maintaining the HTML structure: ```html
LangChain 是一个由语言模型驱动的应用程序开发框架。
```Sure, here is the translated text in simplified Chinese: ```html 使用 LangChain,您可以创建应用程序,筛选存储的文档,提取关键细节,然后将它们整齐地包装成类似聊天的回复。想象一下设置一个检索增强生成器,简称 RAG,就像给您的语言模型提供新的信息片段,当您询问时为它提供增强。这一切都是为了让对话更加丰富,充满新鲜的见解! ```
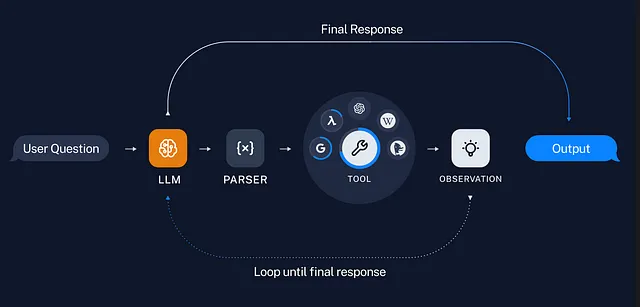
工具是代理、链或LLM用来与世界交互的界面。它们结合了一些东西:
工具的名称
```工具是什么的描述
```工具输入的JSON模式
```工具的结果是否应直接返回给用户
```To translate the text on the webpage you mentioned to simplified Chinese while keeping the HTML structure intact, you would typically follow these steps: 1. **Identify the Text**: Locate the English text on the webpage that needs translation. 2. **HTML Structure**: Ensure you maintain the HTML tags, classes, and IDs as they are essential for the webpage's formatting and functionality. 3. **Translate the Text**: Use a reliable translation tool or service to translate the identified English text into simplified Chinese. 4. **Replace Text in HTML**: Insert the translated Chinese text into the corresponding HTML tags, ensuring that you do not alter the structure of the HTML itself. Here's a basic example of how you might structure the HTML with the translated Chinese text: ```html
这里是工具模块的文档。
您可以在这里找到关于工具模块的详细信息。
` tags. - The `` ensures proper display of Chinese characters. Ensure you review the translated text for accuracy and readability after translation, as machine translations may sometimes require adjustments for clarity and context.
所以,我会使用pyenv来管理我的本地机器上的Python版本:3.9.13
```在创建我们的项目结构之前,让我们开始。
Sure, here's the translation: ```html
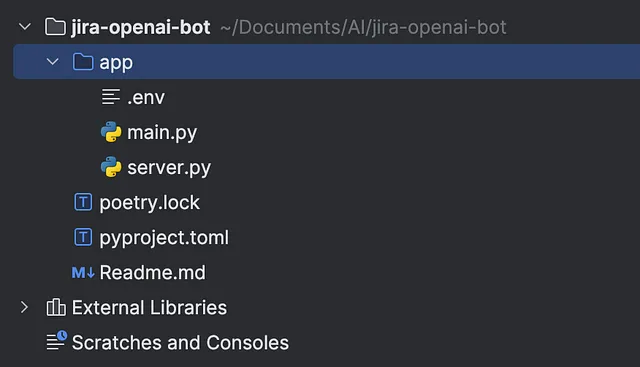
server.py 和 main.py
```
Sure, here's the translation: 然后,我在这里粘贴了我们将在这个项目中使用的依赖项
[tool.poetry]
name = "jira-openai-bot"
version = "0.1.0"
description = ""
authors = ["None"]
readme = "README.md"
packages = [{include = "*", from="app"}]
[tool.poetry.dependencies]
python = "^3.9"
langchain-openai = "^0.0.8"
langchain = "^0.1.12"
openapi-schema-pydantic = "^1.2.4"
python-dotenv = "^1.0.1"
pydantic = "1.10.9"
openapi-pydantic = "^0.4.0"
pyyaml = "^6.0.1"
langserve = {extras = ["server"], version = "^0.0.51"}
python-decouple = "^3.8"
[build-system]
requires = ["poetry-core"]
build-backend = "poetry.core.masonry.api"
Sure, here's the translation: ```html
我们要做的第一件事是创建 fastAPI 服务器,并将其暴露在默认端口 8000 上。
```#!/usr/bin/env python
from fastapi import FastAPI
from typing import Optional
import dotenv
import os
from langserve import add_routes
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from main import *
app = FastAPI(
title="LangChain Server",
version="1.0",
description="A simple api server using Langchain's Runnable interfaces",
)
@app.get("/chat")
async def chat(query: Optional[str] = None):
# Process the query in some way. Here, we just echo it back.
if query is not None:
final_response = jiraAgent(query)
json = {
"query": query,
"aiResponse": final_response,
}
return json
else:
return {"message": "No query provided."}
add_routes(
app,
ChatOpenAI(),
path="/openai",
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
import uvicorn
uvicorn.run(app, host="localhost", port=8000)
Sure, here's the HTML structure with the translated text: ```html
然后我希望你在应用程序内创建另一个名为custom bot的文件,以及一个.env文件,在其中我们将存储我们的OpenAI API密钥和JIRA API密钥
```
这是你的 .env 文件应该看起来的样子
OPENAI_API_KEY=FILL_WITH_YOUR_OWN_VALUES
JIRA_TOKEN=FILL_WITH_YOUR_OWN_VALUES
在main.py中,让我们创建jiraAgent函数。
def jiraAgent(query):
tools = [JiraTicketTool()]
functions = [format_tool_to_openai_function(tool_name) for tool_name in tools]
tool_map = {tool.name: tool for tool in tools}
model_name = "gpt-3.5-turbo-16k"
print('-------- FUNCTIONS ------------')
print(functions)
print('-------- ------------')
print('-------- TOOLMAP ------------')
print(tool_map)
print('-------- ------------')
model = ChatOpenAI(
model=model_name,
temperature=0,
)
print('Query' + '\n ' + query)
response_ai_message = model.predict_messages([HumanMessage(content=query)], functions=functions)
_args = json.loads(response_ai_message.additional_kwargs['function_call'].get('arguments'))
print('Json input Generated by IA'+'\n ')
print(_args)
tool_result = tools[0](_args)
FunctionMessage(name="get_jira_tickets", content=str(tool_result))
response_final = model.predict_messages(
[
HumanMessage(content=query),
response_ai_message,
FunctionMessage(name='get_jira_tickets', content=str(tool_result)),
],
functions=functions
)
print(response_final)
return response_final.content
工具和功能初始化:
functions = [format_tool_to_openai_function(tool_name) for tool_name in tools]: 将每个工具转换为可以被OpenAI函数使用的格式。假设format_tool_to_openai_function是一个执行此转换的实用函数。
```tool_map = {tool.name: tool for tool in tools]: 创建一个字典,将每个工具的名称映射到工具实例。这样可以通过它们的名称轻松访问工具。
```HTML structure for the translated text: ```html
Sure, here's the translation: ```html 模型 = ChatOpenAI(model=model_name, temperature=0): 使用指定的模型名称和温度为0初始化一个ChatOpenAI模型。温度控制模型响应的随机性,0表示最确定性。 ```
Sure, here is the translated text in simplified Chinese while keeping the HTML structure: ```html 查询处理: ```
Sure, here's the translation in simplified Chinese while keeping the HTML structure intact: ```html 提取参数: ``` This HTML will display "提取参数:" in the browser.
现在,OpenAI机器人应该有一种与我们的JIRA API进行通信的方式。让我们为此创建一些工具类。
Sure, here is your text translated into Simplified Chinese while keeping the HTML structure: ```html
WebServiceJiraCaller.py是一个用于调用Jira Web服务的Python脚本。
```class WebServiceJiraCaller:
def __init__(self, base_url, auth_token):
"""
Initializes the WebServiceJiraCaller with the base URL of the JIRA instance
and the authorization token.
:param base_url: The base URL of the JIRA instance.
:param auth_token: The personal access token for authorization.
"""
self.base_url = base_url
self.headers = {
'Authorization': f'Basic {auth_token}',
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
}
def search_tickets(self, fields, jql):
"""
Searches for JIRA tickets based on the given fields and JQL query.
:param fields: A string of comma-separated field names to include in the response.
:param jql: The JQL query string to use for the search.
:return: A response object from the requests library.
"""
params = {
'fields': fields,
'jql': jql
}
response = requests.get(f'{self.base_url}/rest/api/3/search', headers=self.headers, params=params)
return response.text
# Example usage
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Substitute your_actual_base_url and your_actual_auth_token with your actual JIRA base URL and API token
jira_caller = WebServiceJiraCaller('https://mobilityado.atlassian.net', 'your_actual_auth_token')
fields = 'description'
jql = 'assignee IN (currentUser()) AND statusCategory in ("To Do", "In Progress") ORDER BY created DESC'
response = jira_caller.search_tickets(fields, jql)
if response.status_code == 200:
print(response.json()) # Print the JSON response if successful
else:
print('Failed to fetch JIRA tickets:', response.status_code)
Sure, here's the translation: ```html 这将抽象化我们的 Jira API 请求(您可以随后向此类添加更多方法以扩展此功能) ```
Sure, here's the translated text in simplified Chinese within the HTML structure: ```html 现在,OpenAI 必须知道 Jira 规范以及如何调用 Jira API,以及应该填充哪些参数。 ```
这就是 OpenAPI 规范的魔力所在,一个 LLM 如果提供了这个规范,就可以自动从文档中了解如何调用您的自定义 API。典型的 OpenAPI 规范看起来像这样。
openapi: 3.0.0
info:
title: customer
version: '1.0'
servers:
- url: 'https://api.example.com'
paths:
'/customers/{customer_id}':
parameters:
- schema:
type: integer
name: customer_id
in: path
required: true
get:
summary: customer
tags: []
responses:
'200':
description: OK
content:
application/json:
schema:
type: object
properties:
customer_id:
type: integer
customer_name:
type: string
operationId: get-customers-customer_id
description: Retrieve a specific customer by ID
components:
schemas: {}
Sure, here's the translated text in simplified Chinese, while maintaining the HTML structure: ```html
而猜猜看?通过使用FastAPI和pydantic库,您可以轻松地仅使用几行代码创建OpenAPI规范。
```from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
class JiraTicketSearchInput(BaseModel):
jql: str = Field(
...,
description="The JQL string to define the search criteria. Example: 'project = MYPROJECT AND status = \"In Progress\"'"
)
Sure, here’s the translation in simplified Chinese while keeping the HTML structure: ```html
在我们深入了解代码之前,先聊聊pydantic。Pydantic 是一个数据验证和设置管理库,使用 Python 类型注解。它帮助确保你的应用程序使用的数据是有效和正确格式的。
```Here's the translated text in simplified Chinese while maintaining the HTML structure: ```html
Sure, here's the translation in simplified Chinese, while keeping the HTML structure: ```html 字段:此函数用于为模型中的字段提供额外的元数据和验证规则。 ```
在类内部,我们定义了一个名为 jql 的单一字段。
以下是正在发生的事情:
省略号 (...) 表示此字段为必填项。如果未提供 jql 的值,将会发生验证错误。
```描述:此处提供了 jql 字段的可读描述。对于文档目的非常有用,可以被用于生成 API 文档或用户界面的工具。该描述解释了 jql 字段应该包含用于定义搜索条件的 JQL 字符串。提供了一个示例来说明其用法:'project = MYPROJECT AND status = "In Progress"'。
Sure, here's the translated text: 最后,中间件将连接LLM和您的OpenAPI规范。
class JiraTicketTool(BaseTool):
name = "get_jira_tickets"
description = "Used to find tickets assign to current user"
args_schema: Optional[Type[BaseModel]] = JiraTicketSearchInput
def _run(self,jql):
print("request to Jira !")
base_url = 'https://YOURJIRAURL.atlassian.net'
dotenv.load_dotenv()
token=os.getenv('JIRA_TOKEN')
service_caller = WebServiceJiraCaller(base_url, token)
response = service_caller.search_tickets('summary,created,reporter', jql)
return response
def _arun(self, location: str, unit: str):
raise NotImplementedError("This tool does not support async")
最后,当您设置好这个langchain演示后,您应该能够调用不仅是JIRA API,而且还可以调用您自己拥有的另一个私有API。
Sure, here's the translated text in simplified Chinese, keeping the HTML structure: ```html
Github Repo: https://github.com/KevsAlex/jira-openai-bot
要安装 LangChain Python,请执行以下命令:
pip install langchain以下是一个简单的示例:
import langchain
lc = langchain.LangChain()
result = lc.translate("Hello, world!", "en", "zh")
print(result)LangChain Python 包含以下模块:
请参阅详细的 API 文档。
欢迎贡献代码!请参阅贡献指南。
在本节中,您将找到一些用例,以便了解 Langchain 可以用来解决哪些问题。
Langchain 提供了一种强大的平台,用于构建各种自然语言处理(NLP)应用程序。无论您是构建聊天机器人、情感分析工具还是文本分类器,Langchain 都可以帮助您轻松实现您的想法。
通过 Langchain 的语言翻译功能,您可以轻松将文本翻译成多种语言。这对于构建跨语言应用程序或全球化您的产品非常有用。
借助 Langchain 的情感分析工具,您可以快速了解大量文本的情感倾向。这对于分析社交媒体帖子、产品评论或客户反馈非常有用。
Langchain 的文本分类器使您能够将文本按照特定的主题或类别进行分类。这对于自动化信息整理或搜索结果过滤非常有用。
如果您有其他用例或想法,请随时与我们联系。我们很乐意与您讨论如何使用 Langchain 实现您的目标。
```